My web
Solution Delivery Metric Definitions
![]()
Credit Performance
60 Plus to Cure
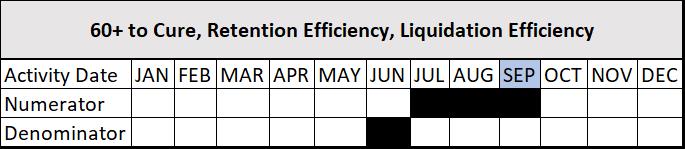
The 60 Plus to Cure metric measures the number of loans 60 or more days delinquent at the beginning of the month that are brought current, paid in full, or repurchased over a three-month reporting period. Active trial modifications less than four-months old that are not converted during the reporting period are excluded from the metric. For example, if a servicer had 120 loans that were 60 or more days delinquent at the end of June, and as of September month end, 25 of these loans were current or paid in full and 20 had active trial modifications less than four-months old (and were not yet current), the 60 plus to Cure rate would be 25% for September Scorecard.
Retention Efficiency
The Retention Efficiency metric measures the number of modifications initiated and completed payment deferrals over a three-month reporting period as a percentage of loans 60 or more days delinquent at the beginning2 of the three-month period. Active trial modifications less than four-months old are excluded from the metric unless the trial meets the definition of the numerator. In this case, the trial is not excluded to ensure the servicer receives credit for the initiated modification.
Six-Month Modification Performance
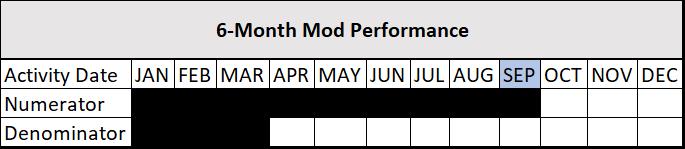
The Six-Month Modification Performance metric measures the number of loan modifications completed between six to eight-months prior that are now less than 30-days delinquent, paid in full, or repurchased, divided by the total number of loan modifications completed and not cancelled in the same time period. This metric uses a rolling three-month total in both the numerator and denominator. For example, the September metric denominator would be all modifications completed in January, February, and March, and the metric numerator would be the sum of January modifications current as of July, February modifications current as of August, and March modifications current as of September Scorecard. Any loan that is paid in full or repurchased between the base month and the scorecard reporting month will be included in the numerator.
Six-Month Payment Deferral Performance
The Six-Month Payment Deferral Performance metric measures the number of payment deferrals completed between six to eight-months prior that are now less than 30-days delinquent, paid in full, or repurchased, divided by the total number of payment deferrals completed and not cancelled in the same time period. This metric uses a rolling three-month total in both the numerator and denominator. For example, the September metric denominator would be all payment deferrals completed in January, February, and March, and the metric numerator would be the sum of January payment deferrals current as of July, February payment deferrals current as of August, and March payment deferrals current as of September Scorecard. Any loan that is paid in full or repurchased between the base month and the scorecard reporting month will be included in the numerator.
Modification Conversion
The Modification Conversion metric measures the number of modification trials initiated between six to eight-months prior that are now completed, divided by the total number of trials initiated in the same time period. This metric uses a rolling three-month total in both the numerator and denominator. For example, the September metric denominator would be all initiated trials in January, February, and March, and the metric numerator would be the sum of January Initiations completed as of July, February initiations completed as of August, and March initiations completed as of September.
2 Retention and liquidation solutions delivered prior to the 60th day of delinquency are included in the metric numerator and denominator and are treated as 60-days delinquent in the Comp.